Last
updated: Tuesday 28th February 2023, 14:21 PT, AD
annedawson.net
Part 1
Introduction to Computer Science,
Programming, and Python
1.1 Computer Systems
1.2 Programming and Problem Solving
1.3 Introduction to Python
1.4 Testing and Debugging
Computer
Systems = Hardware + Software
Hardware, e.g.:
PC
iPhone
laptop
network
Hardware - Main Components
input devices (mouse, keyboard)
output devices (screen, printer)
CPU (microprocessor - the brain)
main memory
secondary memory
Main Memory (RAM)
*
consists of a long
list of memory locations
*
each memory
location has an address
*
each memory
location contains 0s and 1s
*
memory holds chunks
of 8 bits (bytes)
*
a single character,
eg A is held in one byte
*
a large number may
be held in 2 or 4 bytes
Main memory is used when a program is
running
ASCII Code
Capital letter A has an ASCII code
of 65
which in binary looks like: 01000001
Binary numbering system
based on 2 digits, 0 and 1
a binary digit is known as a bit
a group of 8 bits is a byte
half of a byte is known as a nibble
Secondary Memory
Secondary memory (also known as
secondary storage)
is used for permanent storage of data.
Examples of secondary storage:
hard disks, portable hard drives, CDROMs,
USB flash drives
Software
Operating system
You communicate to a computer via its
operating system.
Examples of operating systems:
Windows 7 / Windows 10 / Android / iOS /
Ubuntu Linux
Operating System
Any operating system,
whether it's on a desktop computer,
a laptop or a mobile device, is a complicated
computer program.
What is a computer program? ...
A computer program is
a set of instructions
for the computer to follow.
A program usually has
data input,
and the data is
processed in some way by the program.
A program in operation
is said to be running or executing.
A computer program is software.
Computer Programming Languages
High level languages:
Python, C, C++, Java, PHP (and many, many more)
Intermediate level language:
Assembly
Low level language:
machine code i.e. binary: 01111001
Software to generate executable programs:
Compilers +
Interpreters
A Compiler
- is a computer
program which converts
a high level language
program (source code)
to low level language
(binary code)
which can then be
executed (run).
An Interpreter
- is a computer
program that translates
and executes source
language statements
one line at a time.
Problem Solving and Computer Programming
Algorithms
Program Design
Software Lifecycle
Algorithms
An algorithm is a sequence of precise
instructions
(written in English) that leads to the
solution to a problem.
An algorithm can be compared to a
recipe to bake a cake,
a set of directions to enroll for a
class
or a set of instructions to install an
operating system...
Example Algorithm:
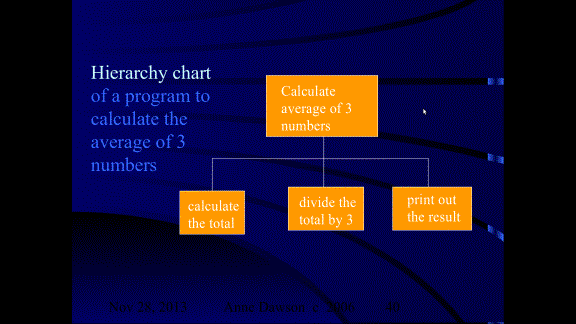
Problem: Find the average of three of numbers
1. get the first
number
2. get the second
number
3. get the third
number
4. add the three
numbers together to calculate the total
5. divide the total by
3 to calculate the average
The
following link contains more information on algorithms:
http://www.annedawson.net/algorithms.html
Computer Science
Computer science can
be defined as the study of algorithms.
An algorithm is a set
of precise instructions to solve a problem.
An algorithm is
converted into pseudocode
which is then
converted into a computer program.
Program Design
problem solving phase
(results in an algorithm)
implementation phase
(results in the program developed from
the algorithm)
Software Lifecycle
1. Problem definition
2. Algorithm design
3. Coding
4.
Testing
5. Maintenance
Table 1 Relative costs of software
systems
System Type Phase costs (%)
________________________________________
Design Coding Testing
Control system 46 20
34
Spaceborne system 34
20 46
Operating system 33 17
50
Scientific system 44 26 30
Business system 44 28 28
Data from Table taken from:
Boehm,B.W. (1981) Software Engineering
Economics, Prentice Hall
Note!
According to the data in Table 1,
when you're developing a computer
program,
you should be spending only one quarter
of the time
on actually typing in the code!
Most of the time should be spent on
design and testing.
Design and Testing
The Design and Testing
stages
in the development of
any computer program
are the most expensive
stages.
Tools for Software Design
Flowcharts
Pseudocode
Hierarchy Charts
Documentation
Flowcharts
Pseudocode
Pseudocode
and algorithm example (for reference only)
Hierarchy Charts
Any paperwork associated
with a computer program
is know as
external
documentation.
Internal documentation
are
any comments you make
in the program
code itself...
Documentation:
Requirements Phase
(what the program has to do)
Design Phase (how it
will do it)
Coding Phase (the code
itself)
Testing Phase (the
test data and results)
Operation Phase (the
user manual)
A
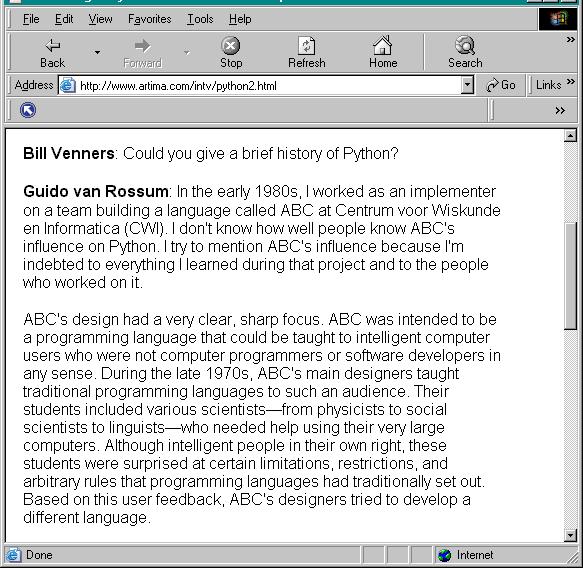
Brief History of Python:
*
invented by Guido
van Rossum in 1990
*
based on the
language ABC
*
named after the BBC
show "Monty Python's Flying Circus"
Python
is:
*
free
*
easy to use and
learn
*
interpreted
*
object oriented
*
small
*
portable
*
extensible
Some short Python
(version 3) example programs:
www.annedawson.net/python3programs.html
Some short Python
(version 2) example programs:
www.annedawson.net/pythonprograms.html
Testing and Debugging
An error in a program is called a bug.
The process of
removing errors is
known as debugging.
Types
of Errors
Syntax error (e.g. incorrect spelling of a keyword)
Run-time error (e.g. trying to divide by zero)
Logic (semantic) error
(e.g. multiplying when you really
meant to divide)
Reference (Appendix A -
"Debugging", page 197, ThinkPython (pdf)
Using
Python
http://www.annedawson.net/Python_Editor_IDLE.htm
This Presentation uses the following program files:
Python version 2
www.annedawson.net/pythonprograms.html
Python version 3
www.annedawson.net/python3programs.html